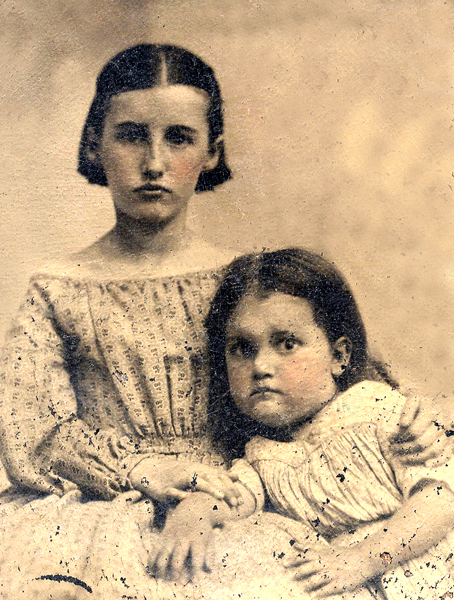 Shortly after the death of seven-month old Jonathan Edwards Blanchard in Cincinnati another child was conceived by Jonathan and Mary Blanchard. Born on January 7, 1841, Mary Avery Blanchard entered life on her mother’s birthday and was so named for her. The eldest of the Blanchard children, Jonathan and Mary sought to provide the best educational opportunities for Mary Avery. For a summer she lived with the John Payson Willistons and enrolled in school in Northampton, Massachusetts. While in school Jonathan wrote his daughter encouraging her to not worry about her grade level but whether she was thorough in her work. When she wrote back in one letter about the handsome men Jonathan wrote back and said she was there to study. Displaying his beliefs about the education of women Jonathan had Mary Avery studying Greek, so that she may read the New Testament, Latin and Mathematics. He told her that “Latin was a glorious language of a glorious people….Love it.” When Mary Avery returned to Galesburg she finished her studies at Knox Female Seminary and became a school teacher in Prospect City, Illinois for a time. When she was seventeen she enrolled at Mount Holyoke College. Jonathan expected much of his eldest child. She had the same impetuous spirit as her father. Engaged for a time to a Mr. Caldwell, someone that Jonathan believed to be less than pious, Mary Avery snapped back that she would marry him and they would go to hell together. However, before they could wed Mary Avery contracted consumption, known today as tuberculosis. Though she was able to make the move to Wheaton with the family when Jonathan assumed the presidency of Wheaton College, Mary Avery died on December 6, 1860, a month before her twentieth birthday. This was the fourth child that Jonathan and Mary Blanchard had lost before reaching full adulthood. Enamored with the work of John G. Fee, Mary Avery bequeathed what little worldly goods she had to his work at Berea College in Kentucky.
Shortly after the death of seven-month old Jonathan Edwards Blanchard in Cincinnati another child was conceived by Jonathan and Mary Blanchard. Born on January 7, 1841, Mary Avery Blanchard entered life on her mother’s birthday and was so named for her. The eldest of the Blanchard children, Jonathan and Mary sought to provide the best educational opportunities for Mary Avery. For a summer she lived with the John Payson Willistons and enrolled in school in Northampton, Massachusetts. While in school Jonathan wrote his daughter encouraging her to not worry about her grade level but whether she was thorough in her work. When she wrote back in one letter about the handsome men Jonathan wrote back and said she was there to study. Displaying his beliefs about the education of women Jonathan had Mary Avery studying Greek, so that she may read the New Testament, Latin and Mathematics. He told her that “Latin was a glorious language of a glorious people….Love it.” When Mary Avery returned to Galesburg she finished her studies at Knox Female Seminary and became a school teacher in Prospect City, Illinois for a time. When she was seventeen she enrolled at Mount Holyoke College. Jonathan expected much of his eldest child. She had the same impetuous spirit as her father. Engaged for a time to a Mr. Caldwell, someone that Jonathan believed to be less than pious, Mary Avery snapped back that she would marry him and they would go to hell together. However, before they could wed Mary Avery contracted consumption, known today as tuberculosis. Though she was able to make the move to Wheaton with the family when Jonathan assumed the presidency of Wheaton College, Mary Avery died on December 6, 1860, a month before her twentieth birthday. This was the fourth child that Jonathan and Mary Blanchard had lost before reaching full adulthood. Enamored with the work of John G. Fee, Mary Avery bequeathed what little worldly goods she had to his work at Berea College in Kentucky.
Upon Mary Avery’s death M. F. Bigney, editor of the the New Orleans paper, The Daily City Item, wrote
Give Me The Harp. She was known as a pious girl and these words were based upon her final earthly words, “Give me the harp I hear.” The poem appeared in Bigney’s The Forest Pilgrims, and other poems published in 1867.
Give me the harp with the sounding strings,
The harp whose tones I hear–
It seems upborne by an angel’s wings,
And unto my bursting heart it brings
The sounds of hope and cheer–
A melody all divine, that springs
From a higher and purer sphere.
Give me the harp, and this trembling hand
Released from the ills of earth,
Shall learn the lays of the better land,
Shall touch the strings with a high command,
And the joy of a spirit-birth
Shall thrill my soul with a rapture grand,
With a fond and holy mirth.
Give me the harp, and I’ll bid farewell
To the fleeting scenes of time ;
With the loved ones gone before I’d dwell,
My harp with theirs should the echoes swell
Of a high immortal rhyme ;
Give me the harp, for I fain would tell
Of release from this world of crime.